Networking and Communication Protocols 101
In a world where everything seems to be getting smarter, from our phones to our thermostats, having a reliable and efficient network connection is crucial. But not all networking and communication protocols are created equal.
First of all, What are Networking and Communication Protocols?
Networking and communication protocols are the underlying signals that enable devices to communicate with each other seamlessly. They dictate how data is transmitted, received, and understood, acting as the essential framework for the exchange of information. These protocols are the unseen liaisons of our interconnected world, facilitating the flow of data between devices, servers, and applications.
Let’s look at a few different protocol types and determine which is best for smart home technology and automation.
WiFi
WiFi is known for its high bandwidth, making it perfect for streaming HD video and supporting multiple devices simultaneously. However, it consumes more power compared to other protocols, which can be a concern for battery-powered devices. WiFi can typically only cover a range of up to 30 feet indoors, depending on the router and environmental factors.
WiFi’s familiar infrastructure consists of a wireless router or access point that connects to your internet connection. This central device broadcasts a network signal throughout a building, allowing devices to connect wirelessly.
We all know that WiFi serves as the backbone of many smart homes, connecting devices like smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and gaming consoles. Its high bandwidth and versatility make it a top choice for applications that don’t mind sacrificing a little more energy.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth, on the other hand, provides moderate bandwidth, which is suitable for tasks like streaming audio and connecting devices in close-range. What sets it apart is its low power consumption, making it an excellent choice for low-energy devices. Bluetooth typically offers a short-range connection, making it ideal for same-room devices.
Interestingly enough, Bluetooth technology doesn’t require routers or single access points as far as infrastructure. Its only mode of data transmission is from host to device, and at a relatively shorter distance.
Bluetooth finds common use in wireless headphones, speakers, keyboards, and mice. Its low power requirements make it a great choice for devices that primarily operate on battery power.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN connectivity operates with low bandwidth, making it perfect for transmitting small amounts of data over its long range of over a mile. This capability paired with its low power requirement make it a top performer when it comes to smart home automation solutions like Quext IoT.
LoRaWAN infrastructure consists of a gateway antenna with connection to end nodes (often battery-powered) and its network server. From there, nodes can send information to each other that will then be processed by the server.
LoRaWAN is perfect for smart home applications using devices like remote sensors, lights, and thermostats. Its long-range capabilities make it a reliable choice for connected devices spread across large areas.
5G
5G, the next generation of wireless technology, offers blazing-fast bandwidth making it suitable for high-data-rate applications like augmented reality and 4K streaming. However, it can be very power-hungry, especially when running data-intensive tasks, which may limit its use in battery-operated devices.
5G infrastructure, closest to the user, involves a network of small-cell base stations that transmit high-frequency signals. These small cells are essential for delivering the promised speeds and low latency of 5G, but they require a dense network deployment.
5G is expected to revolutionize connectivity across a plethora of industries by enabling lightning-fast data transfers and ultra-low latency connections. It's an excellent choice for applications that demand high-speed internet and responsiveness.
Z-Wave
Z-Wave provides a low-to-moderate bandwidth, sufficient for transmitting control commands and status updates. Similar to Bluetooth, Z-Wave is known for its low power consumption and low range, making it ideal for battery-operated smart home devices.
This type of connection acts as a device-to-device connection using low-energy radio waves. Z-Wave networks rely on a mesh topology, where devices act as signal repeaters, extending the network's range. This mesh structure enhances reliability and ensures that even distant devices can communicate effectively.
Z-Wave is commonly used for smart home devices like lights and security systems. Its robust mesh network capabilities allow for reliable communication between devices across a smart home.
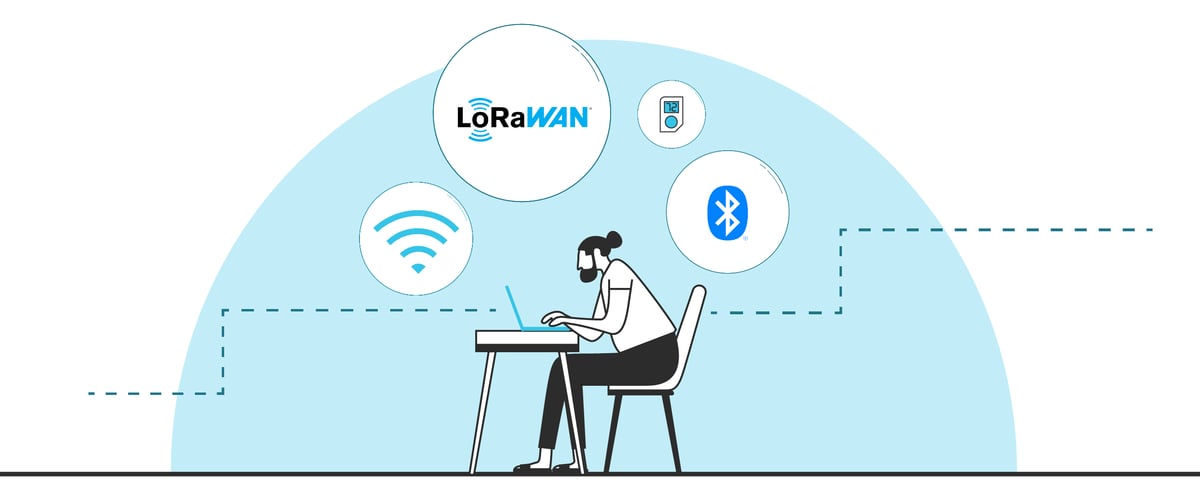
So, Which is Best for Smart Home Technology?
The answer is… not that simple. The best network connection protocol is largely dependent on the delicate balance between the desired solution features and the cost required to achieve them.
WiFi is a strong contender for IoT solutions in smart apartments. Its high bandwidth is a good match for transmitting data across a variety of devices, and its familiar infrastructure ensures easy implementation and integration. Frequently, challenges can arise when WiFi infrastructure isn't already deployed or owned by the multifamily community. WiFi just for the sake of IoT can be expensive, that's why these solutions make the most sense when apartment communities want to buy a managed wifi and smart apartment solution together.
For smart home environments with devices in close proximity, Bluetooth is another great choice. Because of its power efficiency and simple data transmission, it's a competitive candidate for smart home applications, especially those that communicate with battery-powered devices.
When it comes to IoT solutions, LoRaWAN emerges as a top pick. The combination of long-range capabilities and low implementation cost makes it a perfect match for smart home automation in the multifamily industry. Whether its guest access control, remote leak sensors, thermostats, or lights, LoRaWAN can reliably connect devices across large areas.
Some solutions even use a combination of these protocols to ensure seamless connectivity across a range of devices.
For example, Homebase, a partner of Quext’s, runs a smart apartment solution that operates on WiFi and Bluetooth, ensuring its ability to transmit both high and low-data payloads across a smart home ecosystem. For more information on Homebase’s solution, check out this page on their website.
In the case of Quext IoT, LoRaWAN checks all of the boxes for ensuring functionality and efficiency for our specific smart home automation solution. For more information on Quext IoT, visit our product page or check out some of our related blog posts:
The Benefits of Retrofitting Apartment Buildings with an IoT Solution
How to Use Smart Home Automation to Turn Apartments into Smart Homes
How to Use IoT Technology to Create an Energy Management System for Energy Efficient Apartments